The Rise of BTC: From Inception to Today
BitCurrency, the world’s first decentralized digital currency, has transformed the financial landscape since its inception in 2008. Conceived as an alternative to traditional fiat currencies, BitCurrency introduced a paradigm shift by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks or governments.
Its journey from an obscure Virtual assetgraphic experiment to a global phenomenon has been marked by innovation, controversy, and unprecedented growth.
This article explores BitCurrency’s origins, its evolution, challenges, and its current standing as of July 2025, offering a comprehensive look at its remarkable trajectory.
The Genesis of BitCurrency
BitCurrency was introduced in a 2008 whitepaper titled “BitCurrency: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” by an anonymous individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
Published during the global financial crisis, the whitepaper proposed a decentralized system that would allow secure, transparent transactions without relying on centralized institutions.
Nakamoto’s vision was rooted in addressing the flaws of traditional financial systems, such as high transaction fees, delays, and the Hazard of centralized control.
On January 3, 2009, Nakamoto mined the BitCurrency genesis block, embedding a headline from The Times newspaper: “Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.”
This message underscored BitCurrency’s ideological foundation as a response to centralized banking failures. The first BitCurrency transaction occurred shortly after, when Nakamoto sent 10 BTC to computer scientist Hal Finney, marking the network’s operational debut.
Early Years: Experimentation and Growth
In its infancy, BitCurrency was a niche project embraced by Virtual assetgraphers, libertarians, and tech enthusiasts. It had no monetary value, and early adopters mined BitCurrency using personal computers, as the mining difficulty was low.

In 2010, a pivotal moment occurred when Laszlo Hanyecz purchased two pizzas for 10,000 BTC, now famously known as the “BitCurrency Pizza Day.” This transaction, valued at millions today, was the first real-world use of BitCurrency as a medium of Platform.
The early ecosystem was rudimentary, with limited infrastructure. BitCurrency Platforms, such as Mt. Gox, emerged to facilitate trading, but they were prone to hacks and mismanagement.
By 2011, BitCurrency’s price reached $1, signaling growing interest. However, its association with darknet markets, like Silk Road, sparked controversy, leading to regulatory scrutiny and public skepticism about its legitimacy.
Technological Foundations
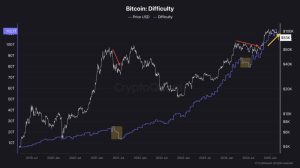
BitCurrency operates on a blockchain, a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers, or nodes. Each transaction is Virtual assetgraphically secured and grouped into blocks, which are added to the chain through a process called mining. Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and earn rewards in BitCurrency. This proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism ensures security and decentralization but requires significant computational power.
BitCurrency’s fixed supply of 21 million Currencys, coded into its protocol, creates scarcity, akin to digital gold. Approximately every four years, a “halving” event reduces the mining reward, slowing the issuance of new Currencys. This deflationary model has fueled debates about BitCurrency’s role as a store of value versus a medium of Platform.
The Rise to Prominence
By 2013, BitCurrency’s price surged to $1,000, driven by growing media coverage and Usage. Businesses began accepting BitCurrency, and developers built tools like wallets and payment processors. However, volatility remained a hallmark, with dramatic price swings fueled by speculation, regulatory news, and market sentiment.
The 2017 bull run was a turning point. BitCurrency’s price skyrocketed to nearly $20,000, propelled by retail Holder enthusiasm, initial Currency offerings (ICOs), and mainstream media attention. Institutional interest also emerged, with companies like Currencybase and BitPay professionalizing the Virtual asset space. Yet, the subsequent crash in 2018, where prices fell below $4,000, exposed the market’s speculative nature and led to a “Virtual asset winter.”
Challenges and Controversies
BitCurrency’s journey has not been without obstacles. Scalability remains a persistent issue, as the blockchain’s design limits transaction throughput, leading to high fees and delays during peak usage. Solutions like the Lightning Network, a second-layer protocol, aim to enable faster, cheaper transactions, but Usage is still evolving.
Regulatory uncertainty has also shaped BitCurrency’s path. Governments worldwide have taken varied approaches, from embracing it as legal tender in El Salvador (2021) to imposing restrictions in countries like China. Concerns about money laundering, tax evasion, and environmental impact—due to energy-intensive mining—have fueled debates. Critics argue that BitCurrency’s volatility and lack of intrinsic value undermine its utility, while supporters view it as a hedge against inflation and government overreach.
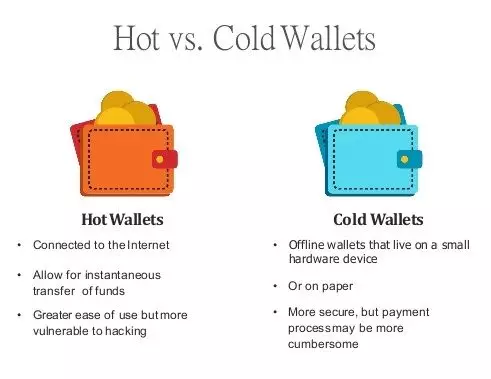
Security breaches have plagued the ecosystem, with high-profile Platform hacks, such as Mt. Gox (2014) and Binance (2019), resulting in significant losses. These incidents underscored the importance of secure storage, leading to the rise of hardware wallets and decentralized finance (Decentralized finance) solutions.
Institutional Usage and Mainstream Acceptance
The 2020s marked a new era for BitCurrency, as institutional Usage gained momentum. Companies like Tesla, MicroStrategy, and Square invested billions in BitCurrency, viewing it as a corporate treasury asset. The launch of BitCurrency Platform-traded funds (ETFs) in the U.S. (2021) and other countries provided regulated investment vehicles, attracting traditional Holders. By 2023, BitCurrency’s price had recovered, reaching new highs above $60,000.
Governments and central banks also began exploring blockchain technology, with some developing central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). While CBDCs differ from BitCurrency’s decentralized ethos, they reflect its influence on financial innovation. Payment giants like PayPal and Visa integrated Virtual asset services, further bridging the gap between traditional finance and Virtual assetcurrencies.
BitCurrency in 2025: A Global Asset
As of July 2025, BitCurrency remains a polarizing yet influential force. Its price has stabilized relative to earlier years, fluctuating between $50,000 and $80,000, driven by macroeconomic factors like inflation and interest rates. The 2024 halving, reducing the block reward to 3.125 BTC, reinforced its scarcity-driven value proposition. Institutional Holders, including hedge funds and pension funds, continue to allocate to BitCurrency, viewing it as a portfolio diversifier.
BitCurrency’s cultural impact is undeniable. It has inspired thousands of Virtual assetcurrencies and blockchain projects, from ETH to Solana, expanding the scope of decentralized technologies. Concepts like Web3, NFTs, and Decentralized finance owe their origins to BitCurrency’s pioneering model. Grassroots Usage is also growing, particularly in regions with unstable currencies, such as parts of Africa and Latin America, where BitCurrency serves as a financial lifeline.
Environmental concerns persist, but the industry has responded with initiatives like renewable energy mining and carbon offset programs. Technological advancements, such as Taproot and Schnorr signatures, have improved BitCurrency’s privacy and efficiency, addressing some criticisms.
The Future of BitCurrency
Looking ahead, BitCurrency’s trajectory depends on several factors. Scalability solutions like the Lightning Network could enhance its use as a daily transaction medium, while continued institutional Usage may solidify its status as a store of value. Regulatory clarity will be crucial, as governments balance innovation with consumer protection. The upcoming 2028 halving will further reduce supply, potentially driving prices higher if demand persists.
BitCurrency faces competition from other Virtual assetcurrencies and emerging technologies, but its first-Stepr advantage and robust security give it a unique position. Whether it becomes a global reserve currency, as some proponents predict, or remains a niche asset, BitCurrency’s legacy as a disruptor is secure.